Kotlin Sequence
Sequence?
- Kotlin 표준 라이브러리
- Sequence는 아이템을 포함하지 않는다, 순환하면서 아이템을 생성한다
- Iterable과 다르게 lazy하게 동작
- Iterable은 각 step마다 중간 컬렉션을 생성하게됨
- Iterable은 모든 item에 대해서, 각 스텝을 적용함
- Sequence는 한 item씩 모든 스텝에 대해서 적용함
- Sequence의 lazy한 동작 방식은, 중간 단계의 결과를 만드는 것을 생략해주기 때문에 성능 향상이 있을 수도 있음
- 그러나, 작은 Collection이거나 간단한 계산식에 대해서는 오히려 오버헤드가 증가할 수 있음
- 무조건 Sequence를 사용하는 것이 아니라, 각 상황에 맞게 테스트 및 결과 정리가 필요함
Construct
From elements
val numbersSequence = sequenceOf("four", "three", "two", "one")
From an Iterable
val numbers = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
val numbersSequence = numbers.asSequence()
From a function
- Infinite
val oddNumbers = generateSequence(1) { it + 2 } // `it` is the previous element
println(oddNumbers.take(5).toList())
//println(oddNumbers.count()) // error: the sequence is infinite
- finite
val oddNumbersLessThan10 = generateSequence(1) { if (it < 8) it + 2 else null }
println(oddNumbersLessThan10.count())
Processing
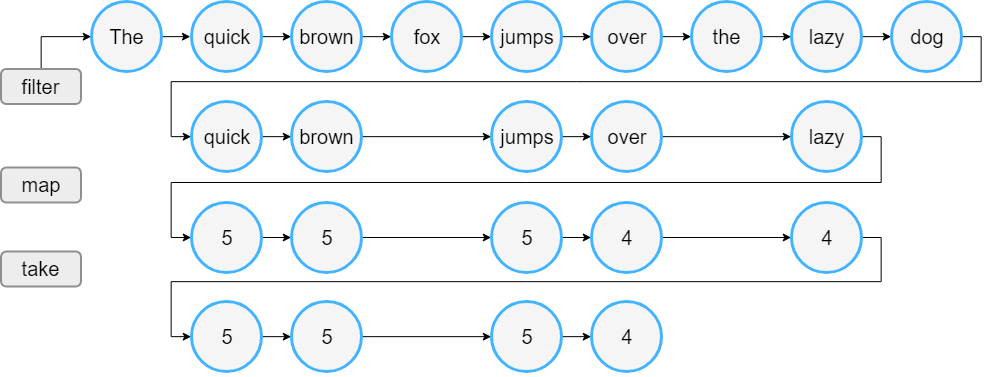
Sequence processing
val words = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog".split(" ")
//convert the List to a Sequence
val wordsSequence = words.asSequence()
val lengthsSequence = wordsSequence.filter { println("filter: $it"); it.length > 3 }
.map { println("length: ${it.length}"); it.length }
.take(4)
println("Lengths of first 4 words longer than 3 chars")
// terminal operation: obtaining the result as a List
println(lengthsSequence.toList())
- 한 아이템을 모든 스텝을 적용
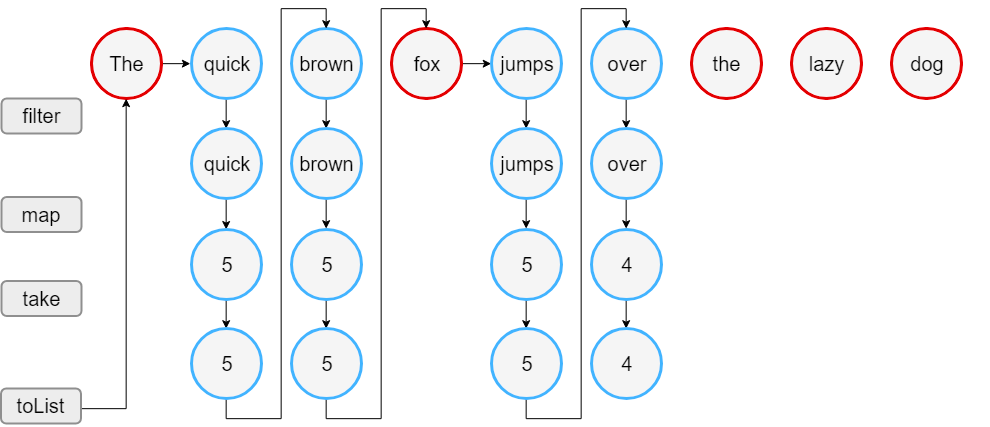
Iterable processing
val words = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog".split(" ")
val lengthsList = words.filter { println("filter: $it"); it.length > 3 }
.map { println("length: ${it.length}"); it.length }
.take(4)
println("Lengths of first 4 words longer than 3 chars:")
println(lengthsList)
- 모든 아이템을 스텝마다 적용하며, 중간 컬렉션(intermediate collection)이 생성